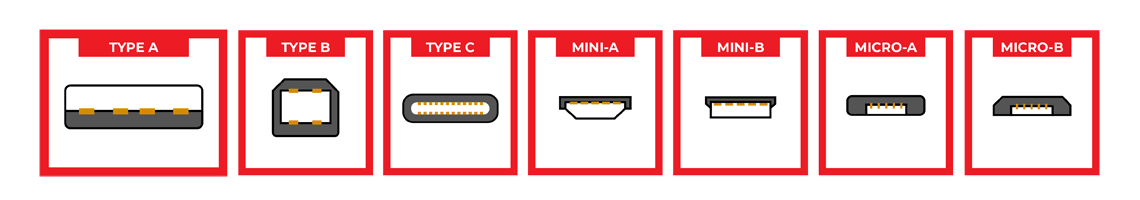
USB Type A connectors: USB-A provides a "downstream" connection for host controllers and hubs, infrequently used as an "upstream" connector on a peripheral device, because a USB host will supply a 5V DC power on the VBUS pin. Used by USB 1.0, 2.0, and 3.0.
USB 1.0: White
USB 2.0: Black
USB 3.0: Blue
USB Type B connectors: USB B provides an “upstream” connection to USB peripherals, such as printer, hub, or other peripheral devices. Connect peripheral devices without the risk of connecting two host computers to one another. USB B type connector is still used today, though it is slowly being phased out in favor of more refined USB connector types.
USB Type C connectors: Adopted by USB 2.0, 3.x, and 4.0 standards, offering a streamlined and versatile connection solution.
USB 1.1 (August 1998): Ranged between 1.5 Mbps to 12 Mbps, labeled as Full Speed.
USB 2.0 (April 2000): Supported up to 480 Mbps, known as High Speed.
USB 3.0 (November 2008): Achieved up to 5 Gbps, termed SuperSpeed.
USB 3.1 (July 2013): Brought in 10 Gbps, known as SuperSpeed+. There's also USB 3.1 Gen 1
(5 Gbps) and Gen 2 (10 Gbps).
USB 3.2 (September 2017): Doubled the speed to 20 Gbps. The nomenclature was adjusted to clarify distinctions among older versions.
USB 4.0 (August 2019): Guaranteed a base speed of 20 Gbps, with an optional 40 Gbps when using a 0.8-meter Gen 3 cable. Integrated features like protocol tunneling, and support for DisplayPort Alternate Mode and 2.0.
USB4 2.0 (October 2022): Released with an astounding 80 Gbps and a groundbreaking 120 Gbps in its asymmetric mode.
USB 1.1 and 2.0 operate in half-duplex mode, allowing for either sending or receiving data at one time.
USB 3.x and 4.0 introduce full-duplex data transmission, making simultaneous sending and receiving of data possible.
Length: USB 2.0 supports up to 5 meters, while USB 3.0 limits the distance to 3 meters. For extensions, consider powered hubs and active USB extension cables.
Pinout: USB 2.0 has four copper wires, while USB 3.x expands to nine.
| SPEC | DATA TRANSFER RATE | CONNECTOR TYPE(S) |
|---|---|---|
| USB4 2.0 | Minimum of 80 Gbps, 120 Gbps is optional | USB-C |
| USB4 | Minimum of 20 Gbps, 40 Gbps is optional | USB-C |
| USB 3.2 Gen 2x2 | 20 Gbps | USB-C |
| USB 3.2 Gen 2 | 10 Gbps | USB-C, USB-A, USB-B, Micro USB-B |
| USB 3.2 Gen 1 | 5 Gbps | USB-C, USB-A, USB-B, Micro USB-B |
| USB 2.0 | 0.48 Gbps | Multiple connectors including USB-C and Mini USB-A |
| USB 1.1 | 0.012 Gbps | USB-A, USB-B |
| Thunderbolt 4 | 40 Gbps | USB-C |
| Thunderbolt 3 | 40 Gbps | USB-C |
Recognizing the USB version your devices support can significantly influence your expectations and overall performance. Remember, the weakest link determines the performance cap of any system. Stay updated to make informed choices.