The Move from Coax to UTP Cable
In the late 1980s, Ethernet networks moved away from bulky coax cabling and started using unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cabling. By the early 1990s, Ethernet networks using UTP cabling became available. Twisted pair runs are widely favored because of their “star” design that allows each individual run to support a maximum distance of 100 meters. UTP runs are made from a combination of 23/24 AWG solid cabling and 24 AWG stranded wire cabling from end to end. Ethernet UTP networks use these wire gauges together to guarantee the best performance.
One of the most common cabling components in a UTP Ethernet channel is the patch cable. Modern networks use hundreds and thousands of patch cables. They are usually installed in data cabinets, relay racks, and enclosures. At one point, patch cables were only assembled with 24 AWG stranded wire raw cable. However, as networks grew to support higher bandwidths, more and more patch cables had to be used in tight spaces and density demands increased. Because of these two developments, the network industry eventually demanded UTP cabling with a smaller wire gauge, and a slimmer 28 AWG stranded patch cable was developed.
28 AWG Patch Cable
28 AWG patch cables have been around for many years. They have been steadily gaining popularity because they provide better port visibility, improve cooling and airflow, and save space in data cabinets and enclosures. In the latest TIA-568.2-D standard for “Balanced Twisted Pair Telecommunications Cabling and Components Standard,” released in September 2018, the cabling industry officially recognized 28 AWG stranded patch cables as acceptable for use in networks. However, the industry had to make some adjustments for computing the total maximum length of the channel after they found 28 AWG patch cable acceptable.
How to Compute Maximum Ethernet Channel Distance
The maximum Ethernet channel distance is 100 meters from end to end. The maximum distance is based on using 90 meters 23 or 24 AWG solid horizontal cable along with 10 meters of 24 AWG stranded patch cable. Horizontal cable may vary between 23 and 24 AWG, depending upon the cable category, but the patch cable for the channel is always 24 AWG stranded wire.
You can compute the maximum Ethernet channel distance with the formula that appears after this paragraph. You can compute the maximum allowable stranded patch cable for an Ethernet channel through the de-rating factor value in this formula. The de-rating factor enables you to calculate the maximum legal channel length when the solid and stranded cable in the channel varies. Being able to do this is important, since stranded cable attenuates more than solid cable, which increases signal loss and can affect the channel if you use too much stranded cable.
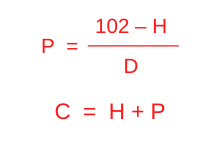
H = the length (m) of the permanent link (horizontal cable)
D = the insertion loss de-rating factor for the patch cable
P = the length of patch cables allowed
C = the total length of the channel
De-Rating Factor
28 AWG stranded: 1.95
24 AWG stranded: 1.2
23/24 AWG solid: 1.0
Here is an example of a full-length 100-meter Ethernet channel using 90 meters of solid horizontal cable and 10 meters of 24 AWG stranded patch cable:
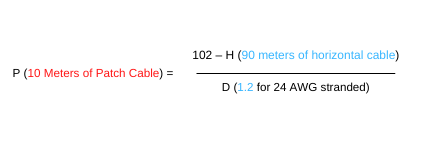
Now add the computed 10 meters of 24 AWG patch cable to the 90 meters of solid horizontal wire, and you get a channel length of 100 meters:

The industry had to adjust this calculation when techs started using 28 AWG patch cables in the channel. Since 28 AWG stranded wire is smaller than 24 AWG stranded wire, the signal loss increases, shortening the overall channel. So, you need to use a new de-rating factor if you are using 28 AWG assemblies in a channel. The de-rating value for 28 AWG stranded patch cable is 1.95.
If you still want to run 90 meters of solid horizontal cable and need to compute how much 28 AWG stranded patch cable you can use, refer to the second example:
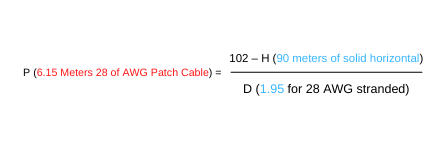

In a UTP run, there is a 3.85-meter difference between using 24 AWG patch cables and using 28 AWG patch cables, with a fixed 90 meters of solid horizontal cable. You can use some basic algebra to figure out the maximum amount of solid horizontal cable that’s allowed if you have a specific length of patch cable required in your run.

Product Engineer
Steve Molek has 27 years’ experience in the cabling and connectivity data communication industry. He started his career as a Technical Support Representative and now works as a Project Engineer for Black Box. As a Product Engineer, his primary focus is evaluating and testing all new cabling and connectivity products for sale by Black Box and training our inside technical support and sales teams. Steve also works directly with our domestic and international OEM suppliers as well as several nationally recognized third-party testing labs. Steve holds a B.S. degree in Mathematics and Computer Science from California University of Pennsylvania and an MBA from Waynesburg University.